
Alongside my passion for teaching, I am deeply involved in 3D printing as a hobby, specializing in low-poly prints. I am proficient in slicing software and adept at managing both resin and FDM printers. My expertise extends to creating 3D print-ready models and understanding the intricate nuances of 3D printing technology.
My Gear
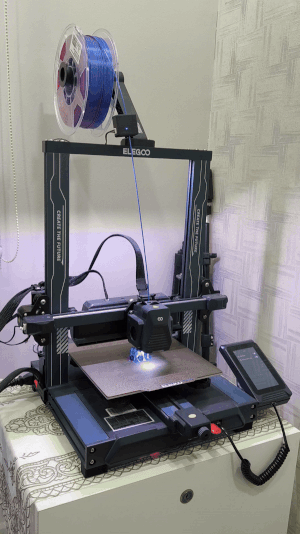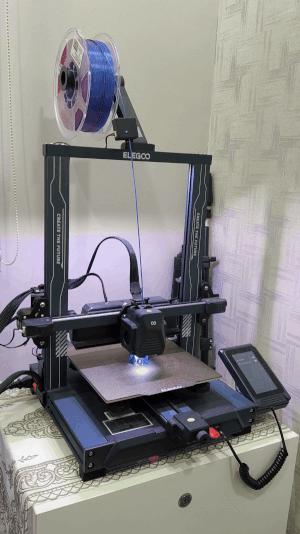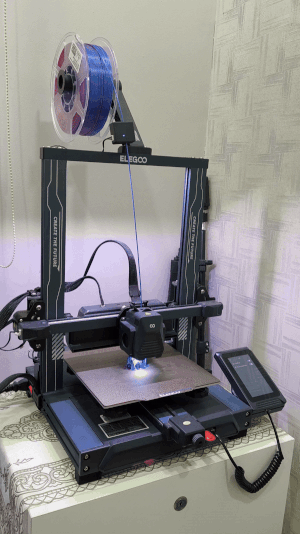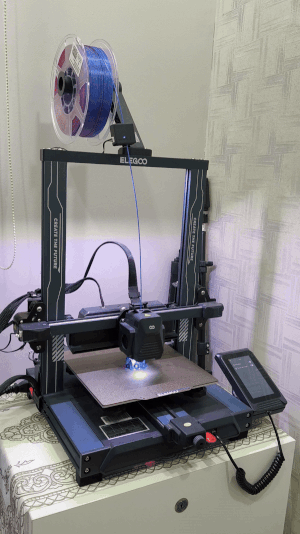
Printer: Elegoo Neptune 4 Pro (FDM)
Proficient Materials: PLA, PetG, PLA+, PLA Silk, PLA Matte and ABS
Design Expertise: Blender 3D, Fusion 360 and TinkerCAD
Slicing Expertise: Orca, Ultimaker Cura, Lychee Slicer and PrusaSLicer
What it takes to 3D Print?
Suren's 3D printer in action...
-
Print Quality and Resolution: Achieving high-quality, detailed prints can be challenging due to the layer-by-layer nature of FDM, which may result in visible layer lines and lower resolution compared to other 3D printing methods.
-
Material Limitations: FDM printers primarily use thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, and PETG. Each material has its own set of challenges, such as warping, stringing, and varying levels of adhesion.
-
Print Speed: FDM printing can be relatively slow, especially for complex or large models. Increasing the print speed can compromise the print quality.
-
Warpage and Adhesion Issues: Ensuring proper bed adhesion and minimizing warping, particularly with materials like ABS, can be difficult. This often requires a heated bed, enclosure, or the use of adhesives and build surfaces.
-
Support Structures: Overhangs and complex geometries often require support structures, which can be time-consuming to remove and may affect the surface finish of the print.
-
Mechanical Failures: Issues like nozzle clogging, filament jams, and extruder problems can interrupt printing and require troubleshooting and maintenance.
-
Post-Processing: FDM prints often require significant post-processing, such as sanding, smoothing, and painting, to achieve a polished final product.
-
Dimensional Accuracy: Maintaining precise dimensions and tolerances can be challenging due to factors like thermal expansion and contraction of the filament during printing.
-
Noise and Odor: FDM printers can be noisy, and some materials (like ABS) emit odors during printing, which can be unpleasant and require ventilation.
-
Calibration and Maintenance: Regular calibration and maintenance are essential to ensure consistent print quality, including bed leveling, extruder calibration, and replacing worn components.